
Detection of a Highly Ionized Outflow in the Quasiperiodically Erupting Source GSN 069
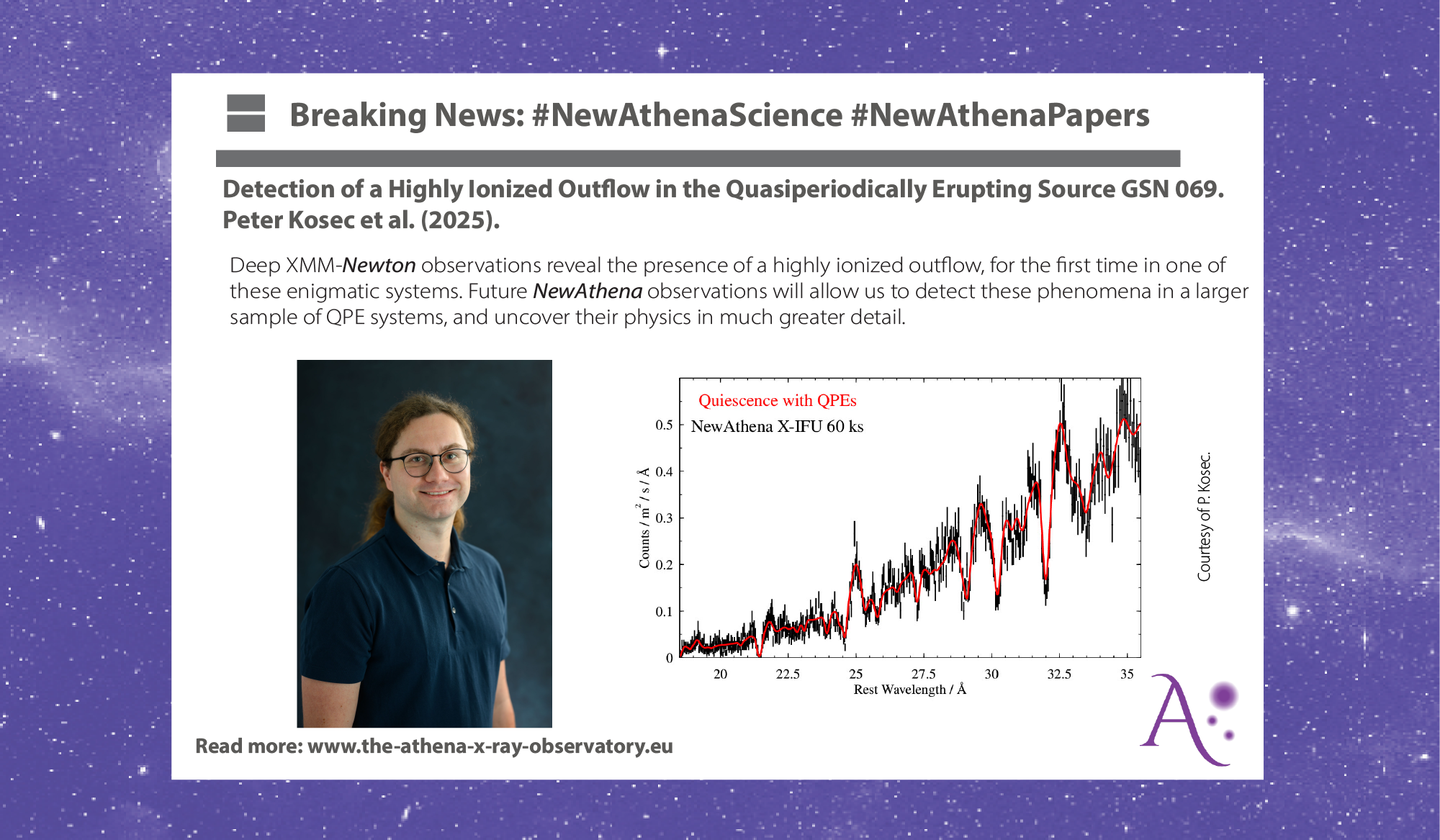
Caption: Spectral simulation of a 60 ks NewAthena X-IFU observation of GSN 069. The simulation shows that the absorption and emission lines of the outflow in GSN 069 can easily be detected and resolved by NewAthena in this brief exposure time.
By P. Kosec
Quasi-periodic eruptions (QPEs) are high-amplitude, soft X-ray bursts recurring every few hours, associated with supermassive black holes. Many interpretations for QPEs were proposed since their recent discovery in 2019, including extreme mass ratio inspirals and accretion disk instabilities. But, as of today, their nature still remains debated. We performed the first high-resolution X-ray spectral study of a QPE source using the RGS gratings onboard XMM-Newton, leveraging in total nearly 2 Ms of exposure on GSN 069, the first discovered source of this class. We resolved several absorption and emission lines including a strong line pair near the N VII rest-frame energy, resembling the P-Cygni profile. We applied photoionization spectral models and identified the absorption lines as an outflow blueshifted by about 2500 km/s. The emission lines are instead redshifted by up to 3000 km/s, and likely originate from the same outflow that imprints the absorption features, and covers the full 4π sky from the point of view of GSN 069. From the properties of the outflow we derived limits on its location which indicate that the outflow is connected to the recent complex, transient activity of GSN 069 that began around 2010.
Thanks to the very high spectral resolution and effective area in the soft X-ray band (0.3-2.0 keV) of X-IFU, NewAthena will be the perfect instrument to study these newly discovered outflow phenomena in QPE sources. We performed a spectral simulation of a NewAthena observation of GSN 069, which shows that just a 60 ks exposure is more than sufficient to detect the outflow at very high statistical significance, greatly exceeding the quality of the current 2000 ks exposure with XMM RGS. NewAthena will thus allow us to search for and detect outflows in QPE systems significantly fainter than GSN 069 (which is most of them). At the same time, thanks to the increased data quality, NewAthena will be capable of performing much finer time-resolved analyses of the QPE systems, allowing us to understand how the outflow properties change with time. Tracking these changes with time-dependent photoionization models will constrain the exact distance of the outflow from the black hole, thus revealing its mass outflow rate, energetics, and its connection to the QPE events.

