
Constraints on the ultrafast outflows in the narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy Mrk 1044 from high-resolution time- and flux-resolved spectroscopy
By Yerong Xu
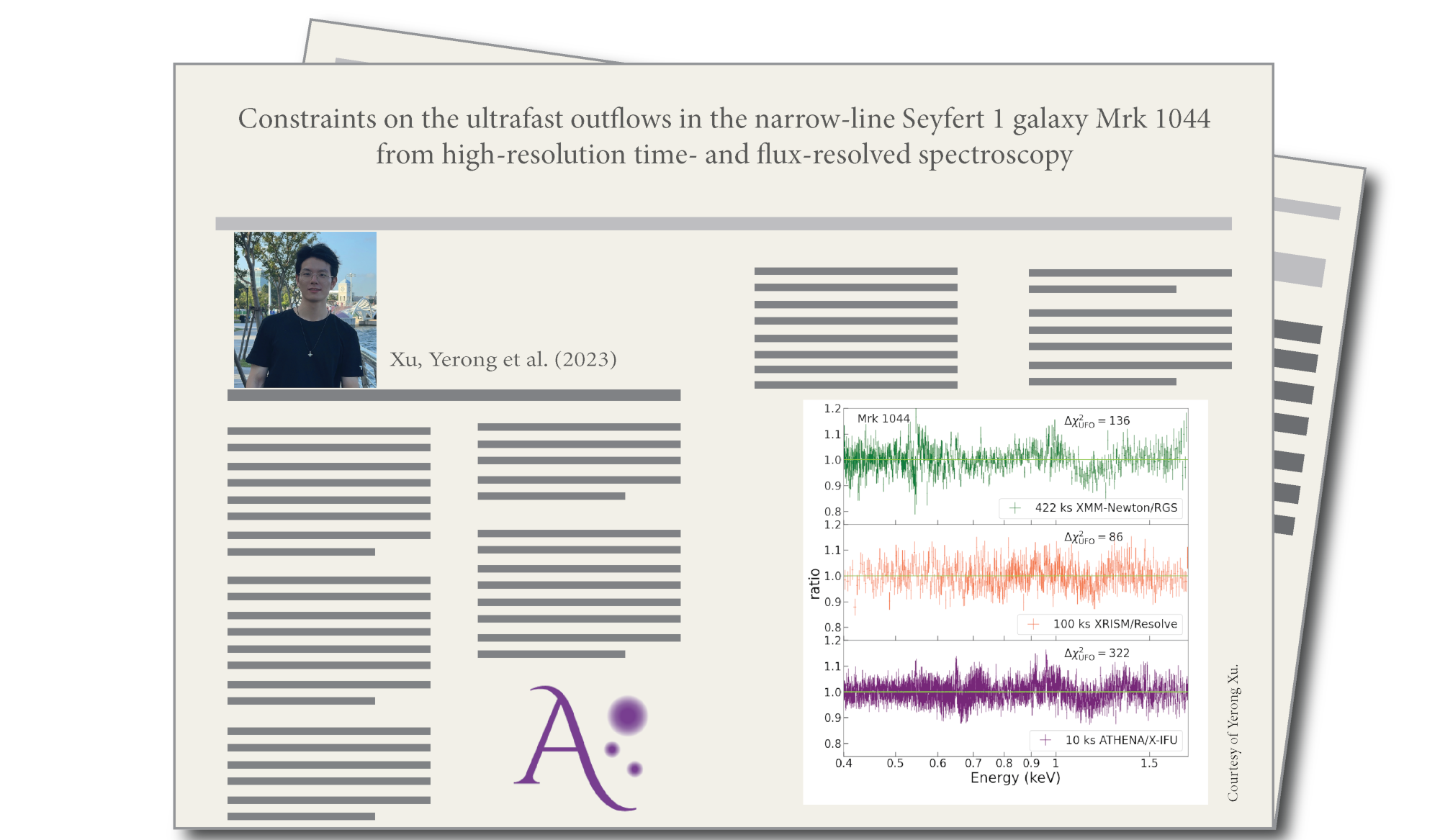
Ultra-fast outflows (UFOs) are regarded as a promising candidate for driving the active galactic nuclei (AGN) feedback on the host galaxy, while their nature and launching mechanism are not yet fully understood. We perform a time- and flux-resolved spectroscopy on four XMM-Newton/RGS observations of a highly-accreting narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxy, Mrk 1044, to study the nature of UFOs. The most important discovery is that the UFO responds to the source variability quickly and might be accelerated by the radiation pressure. Our simulations show that Athena/X-IFU can reach over twice better detection statistics of UFO with only a several per cent exposure time of XMM-Newton/RGS, allowing us to effectively trace the UFO evolution and avoid the spectral broadening due to the flux-resolved spectroscopy. With the unique combination of unprecedented effective area and spectral resolution, Athena will revolutionize our understanding of UFOs and resolve the debates about the UFO launching mechanisms.

