
First Configurational Study of the CryoAC Detector Silicon Chip of the Athena X-Ray Observatory
By Lorenzo Ferrari Barusso
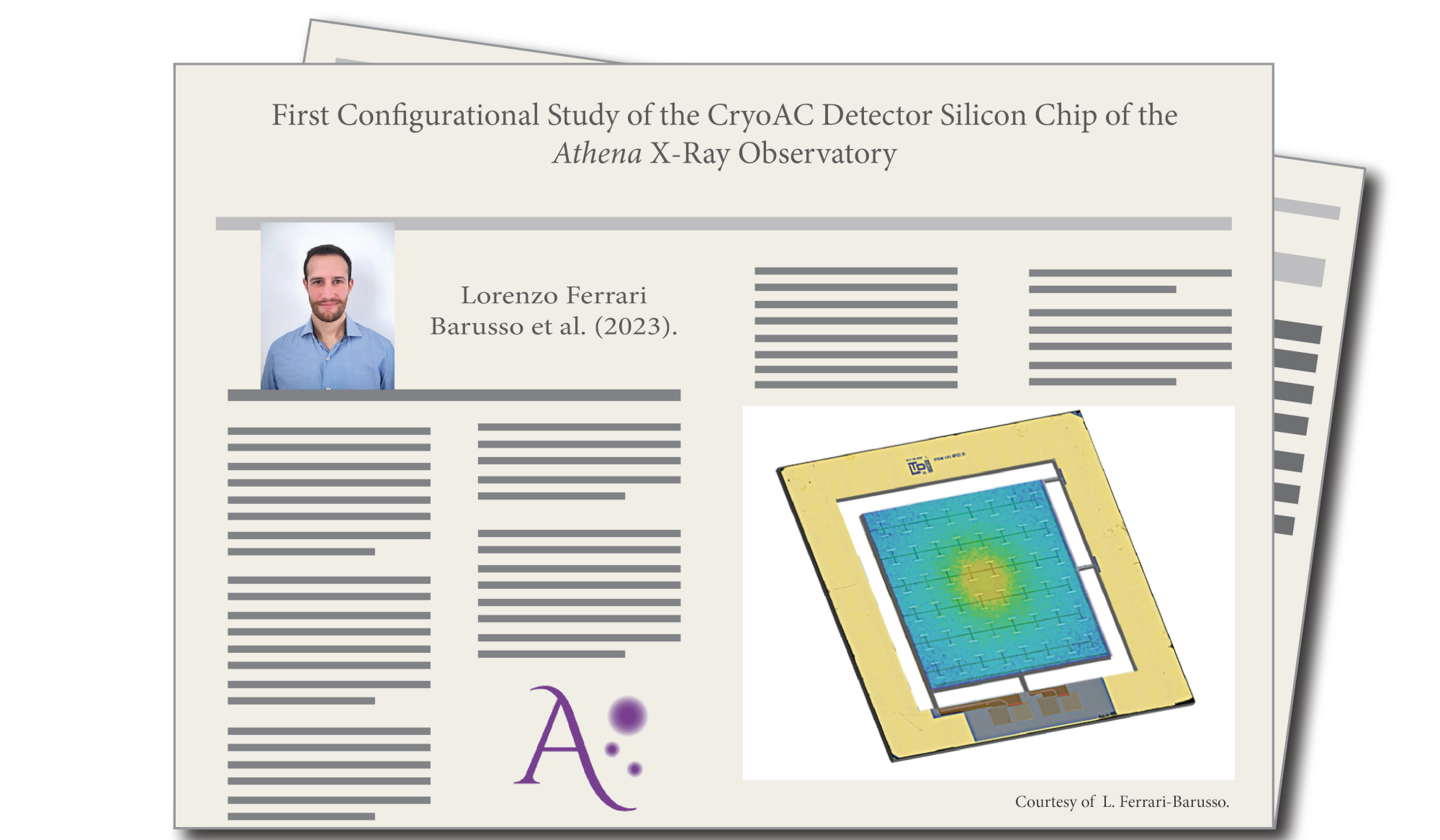
The 50 mK cryogenic focal plane anticoincidence detector of the Athena X-ray observatory X-IFU (CryoAC) is a silicon-suspended absorber sensed by a network of 400 Ir/Au transition edge sensors (TES) and connected through silicon bridges to a surrounding silicon frame plated with gold. The device is shaped by deep reactive ion etching from a single silicon wafer of 500 μm. In operating test of prototypes of the demonstration model of the CryoAC, we have highlighted the importance of the phonon hot spot in the signal generation. A fast response to the cosmic particle of a large area of about 4 cm2 and a thin 0.5 mm silicon absorber covered by a TES array can be assured by matching the TES array configuration to the size and properties of the hot spot. In this article, we present the preparatory study of a proposal for measuring the phonon hot spot that is predicted by the particle-absorber interaction model. This will increase the capability of the CryoAC detector for the Athena/X-IFU.
