
An In-depth Study of Particle Background of X-ray Detectors
By Esra Bulbul
The Athena Wide Field Imager (WFI) background team has recently completed an in-depth study of particle background of XMM-Newton EPIC-pn in preparations for improving background characterization and reduction of WFI’s DEPFET detectors. The PN small window mode (PN SWM) frame time of EPIC-pn (5.67 ms) is similar to the Athena WFI default frame, allowing the team to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between the energetic charged particle events which are rejected by the default processing and the secondary photon and electron interactions which will comprise the instrumental/unfocused background of WFI.
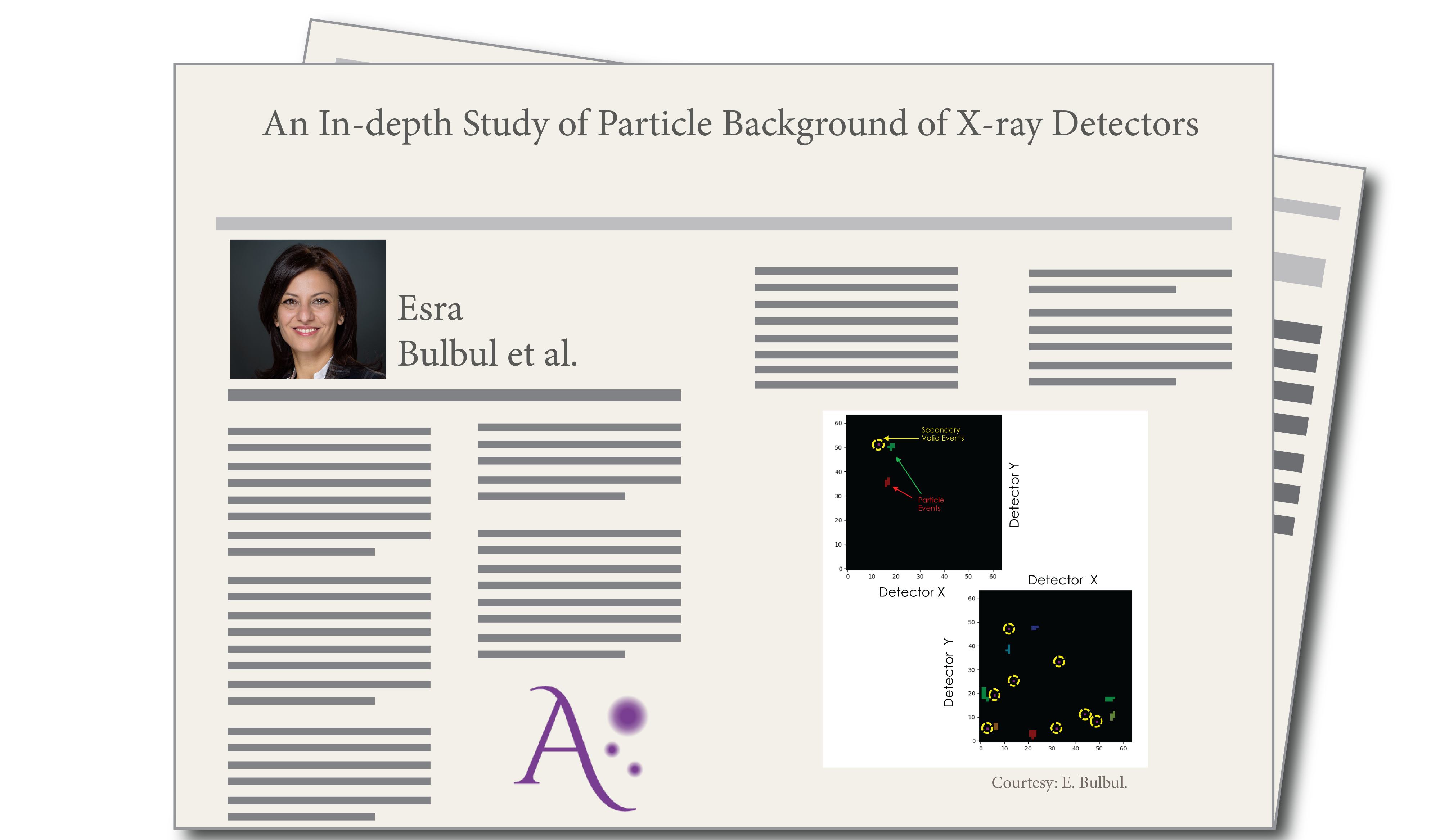
The team examined the long-term variability of the unfocused background observations performed with the filter-wheel closed and Minimum Ionizing Particles (MIP) rejection disabled. The PN SWM filter-wheel closed observations do not allow photons from celestial sources or soft protons to reach the focal plane. The particle-induced background of X-ray observatories is produced by energetic (~1 GeV) Galactic cosmic ray (GCR) primary protons, electrons, and He ions. The interactions of these primary particles with the detector environment produce secondary particles that mimic X-ray events from celestial sources and are much more difficult to reject since they mimic sky X-rays to the default event processing algorithms. The team confirmed an early finding that that GCR flux is modulated in anti-correlation with solar activity.
While Earth’s magnetic field provides a varying degree of geomagnetic shielding from the GCR particles, the flux level varies by a factor of two. More importantly, the authors demonstrated that X-ray-like background events are spatially correlated with the primary particle interaction.
They also found that the spectrum and pattern fractions of secondary particle events are different from those produced by cosmic X-rays. A similar result was obtained with GEANT4 modeling of the charged-particle interaction with the WFI performed by MPE, Milan, MIT, and the Open University (UK), thus validating these simulations. Further investigation of the charged-particle interactions may allow the team to develop advanced algorithms to reduce the instrumental background in the Athena WFI and in other future missions with pixelated silicon X-ray detectors.

