
Soft proton scattering at grazing incidence from X-ray mirrors...
By Roberta Amato
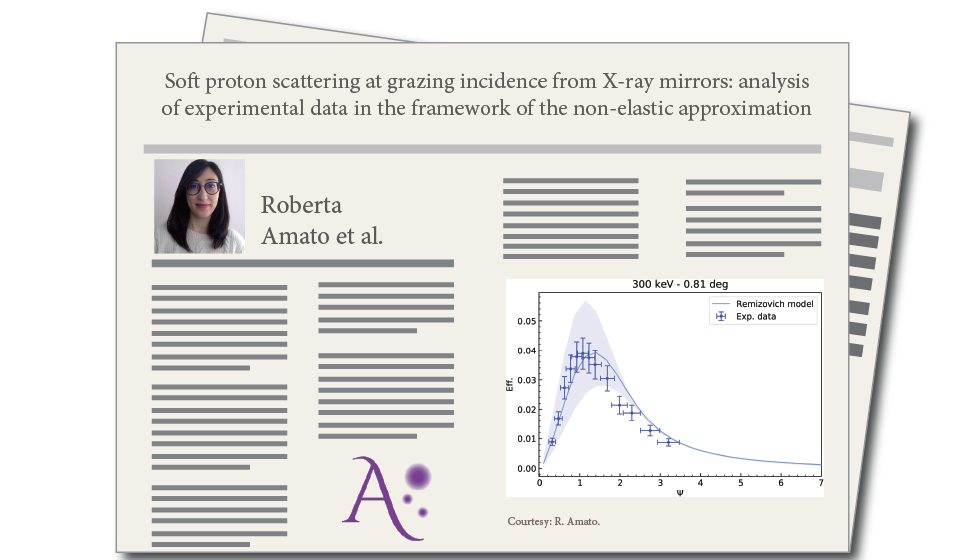
Soft protons impinging at grazing incidence and pseudo-focused by X-ray mirrors constitute a variable and unpredictable component of the non X-ray background of X-ray observatories with grazing incidence optics. A correct estimation of their flux at the focal plane is essential for those missions which aim at observing faint sources at large red-shifts, like Athena. For this reason, we have developed a semi-empirical analytical model, through a comparison between the solution for the reflectivity of grazing protons in non-elastic approximation proposed by Remizovich et al. (1980) and the few available experimental measurements on XMM-Newton and eROSITA mirror samples. The model enables us to estimate the scattering efficiency of protons at grazing incidence, taking into account their energy losses. On-going laboratory measurements on Silicon Pore Optics will improve the model and will allow us to to give a more precise evaluation of the soft proton flux at the Athena focal plane using specific tools such as, for example, a proton response matrix.

