
Impact of the Absorber-Coupling Design...
By Martin de Wit
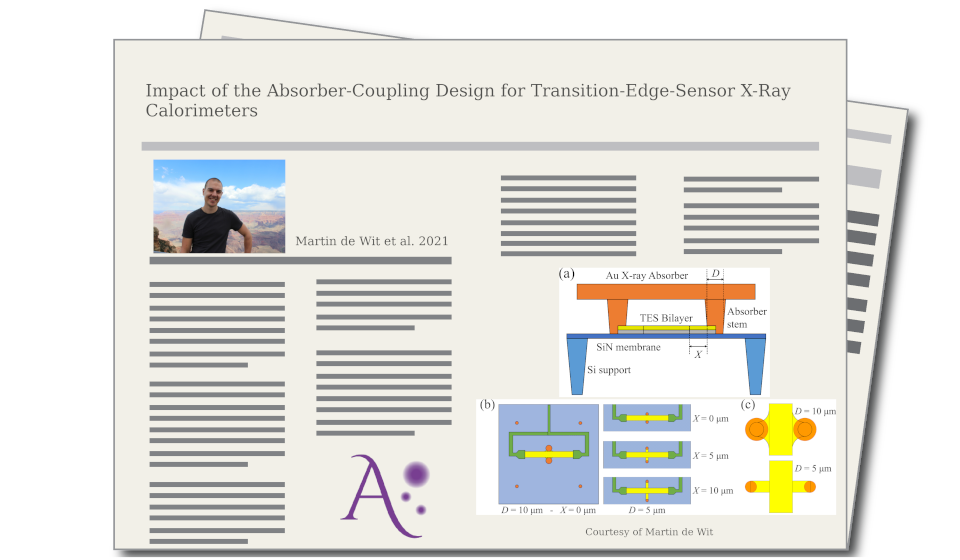
The X-ray Integral Field Unit (X-IFU) is ESA's revolutionary X-ray spectrometer to be mounted on the Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics (Athena). It intends to combine high spectral resolution (the ability to distinguish different photon energies) with high-quality imaging. To meet these ambitious goals, every aspect of the pixels has to be optimized. For X-IFU the pixels are based on Transition Edge Sensors (TESs), extremely sensitive thermometers due to the sharp resistive transition between a metals normal and superconducting state. In this paper, we describe a study into the impact of one of the finer details of the TES design, namely the geometry of the structure that couples the TES to its X-ray absorber. While this might sound like a trivial aspect of the design, by studying four different geometries we have found that minor changes to this design can have a large impact on the detector signal-to-noise-ratio and the smoothness of the superconducting transition. In particular, this last observation might allow us to design better detectors to satisfy the demands for X-IFU.
